DevOps
Gerelateerde artikelen
DevOps – The Origin

In recent years, many organizations have experienced the benefits of using Agile methods such as Scrum and Kanban. The software is delivered faster and quality increases while costs decrease. A major disadvantage is that Agile development is in conflict with the traditional service management, in terms of information management, application management and infrastructure management.
This is mainly because the service organization is unable to meet the agile developers’ flexibility requirements. But a more important reason is that the gap between development and service management has therefore become much bigger. The Agile culture of speed, communication and collaboration is in not in line with that of the traditional control-based service management organization. The consequence is that the development teams are able to deliver software quickly but the software cannot be taken into production quickly. This problem requires a fundamental change in the way of cooperation.
DevOps – What is it?
The solution to this problem has been found in the Dev (Development) Ops (Operations) approach. Both worlds are merged into one team, thus sharing the knowledge and skills and matching the working methods. This has major consequences for the way in which service management processes need to be organized. However, the advantage is a high level of control with a high time to market. DevOps is not a unified concept like ITIL. For example, Gartner recognizes six DevOps streams. Any flow interprets DevOps in a different way.
DevOps – Common Features
However, there are generic aspects to recognize in these streams. The following features characterizes the use of DevOps:
Human: Culture, behaviour, development, cooperation, scalability and affinity are terms where DevOps is about.
Methods: An important aspect of DevOps is to think and work Agile, whether it’s Agile Scrum, Kanban, or another variant. But also, Lean thoughts and Kaizen are reflected in various publications.
Resources: The resource side is mainly highlighted from the way products are produced. So aspects such as versioning, integration, deployment, delivery are discussed. This focuses on the automation of these aspects.
DevOps – A framework
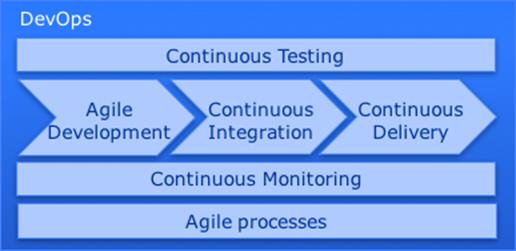
Unlike frameworks like ITIL, DevOps is not defined as a set of best practices and processes. Nevertheless, there is some coherence of the concepts to be recognized. This is illustrated in Figure 1.
This ‘framework’ is not the ‘DevOps’ framework, but a ‘DevOps’ framework. This framework only indicates which concepts can be recognized and to some extent have a relationship. Below is a brief explanation per concept.
DevOps – Continuous Testing
Continuous Testing is a test approach that assists test management throughout the development process including the unit tests, integration tests, system tests and acceptance tests. Preferably, the test cases are written earlier than the software and in addition to performing the usual test types, test management is highly automated. This requires a high degree of integration of requirement management, software configuration management and test management.
DevOps – Agile Development
The term Agile Development refers to embracing Agile’s thinking for software development within DevOps. The Agile Manifesto is of course an important place. Various Agile approaches can be used for this purpose, such as Scrum, Kanban and XP.
DevOps – Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration provides best practices to allow many programmers to run an application at a time, combining the source code, verified (static test cases), compiled and tested (dynamic test cases) at high frequency.
DevOps – Continuous Delivery
Continuous Delivery focuses on the high-frequency throughput of the development test-acceptance-production environments. Based on a high degree of automation, an extreme time to market is offered up to an implementation period of some minutes.
DevOps – Continuous Monitoring
Continuous Monitoring is an essential part of DevOps, which not only monitors software (resources) but also developers (people) and development processes (methods). The resources are measured continuously in all environments to find errors as early as possible. The people are measured in terms of competence development (knowledge, skills and attitude) and the method includes measuring velocity (processing capacity) and efficiency.
DevOps – Agile processes
Agile processes is the focus area that indicates what adjustments in the standard management processes are required to meet the Agile development methods.
DevOps – Conclusion
DevOps is not a set of best practices it’s not a model, it’s not a new hype. DevOps is more a movement based on a number of basic principles in order to better match customer requirements in terms of time-to-market and added value. These principles include cultural aspects, cooperation aspects, automation through tooling and scalability of cooperation.
Discuss with us about this article on LinkedIn.
More information
Related Books:
DevOps Best Practices, ISBN: 9789492618078
Agile Service Management with Scrum, ISBN: 9789071501807
Related training sessions:
- DevOps Foundation
- DevOps in practice
- DevOps Master
- Masterclass DevOps Operations
- Masterclass DevOps Application Development
- Masterclass DevOps Architecture
Related Article:


Mogelijk is dit een vertaling van Google Translate en kan fouten bevatten. Klik hier om mee te helpen met het verbeteren van vertalingen.
Laatste artikelen
- De IT-offerte: Waar moet je op letten bij Software en SaaS?
- De ICT-checklist voor het moderne kantoorgebouw
- De paradox van Cloud FinOps Governance: kostenbeheersing in de cloud
- De mens als AI agent: van meester naar slaaf
- Exploratief testen: Agile softwaretesting zonder testscripts
- DRY Principe: Fundament voor Schone Code en Onderhoudbare IT
- Citizen Developer Governance: Veilige Low-Code/No-Code voor medewerkers en compliance
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): Noodstroomvoorziening voor IT-Infrastructuur
- De Cloud Security Baseline: 10 kritieke auditpunten voor AWS, Azure en GCP
- Model Drift: de onvermijdelijke veroudering van AI-modellen
