DevOps Architecture – Organisation patterns
Gerelateerde artikelen
Organisation patterns Introduction
This article describes some organisation patterns for organizing DevOps teams.
Organisation patterns Definitions

Service desk: A service desk is a Single Point of Contact (SPOC) between the customer and the service provider. Most of the time the communication concerns questions, service requests, incidents, feature requests and complaints. For DevOps teams a service desk is important since it enables a DevOps team to focus on their process.
Change control:
Within each DevOps team there is a form of a tollgate to accept a feature and to promote it. This control is summarized in the term “change control”. In practice, this can be organized in many alternative ways such as a product owner, a gate keeper, a Change Advisory Board (CAB). It is also possible to choose different “Change controls” for one DevOps team depending on the risk and impact of the feature.
Vertical feature split:
In the ideal world one DevOps team is capable to realize a feature request autonomous. This means that there is no dependency of another DevOps team or other kind of organizational unit of work like an infrastructure department. The advantage of this approach is that there is very few need to communicate and align with other teams. The disadvantage is that such a team must have a broad set of knowledge and know how.
Horizontal feature split:
In some service organisations, there is a need to have specialized DevOps teams that only can perform a part of a feature request. In that case for one feature request more DevOps teams have to work together to release the new of changed objects. The advantage is that such a teams have very deep knowledge of the products they use and are able to deliver high quality. The disadvantage is that all most every feature must get a Go-life by at least two or more teams.
Organisation Pattern:
A pattern is a generic solution for a generic and recurring problem. By analysing the problems a DevOps team faces and the way they solve their problem, patterns can be created and shared with other DevOps teams by telling stories. This article gives some patterns for the way in which DevOps teams can be organized.
Organisation patterns Concepts
Feature splitting:
There are two ways to subdivide features across DevOps teams, namely a vertical feature split and a horizontal feature split. In general the preference is has a vertical split because less alignment between the teams is required. However, this is not always possible, for example due to the complexity of the application and / or the infrastructure. This article will mention per pattern which type of feature splitting is used.
Organisation patterns
There are various patterns to be identified when organizing DevOps teams. Each pattern has advantages and disadvantages. This article discusses three patterns briefly namely:
- The business line pattern. This pattern only have DevOps teams that work for one business line.
- The portfolio pattern. This pattern shows how to split the work of DevOps team based on the applications that exist in the application portfolio.
- The information value chain. This pattern is especially applicable for information providers which translate information lakes into information reports.
Each of these three patterns do use the functions of the service desk and the change control. But per pattern the usage of the vertical / horizontal split is different. The choice for a pattern can have a huge impact om the performance of the DevOps teams and the quality of their work.
Business line organisation pattern
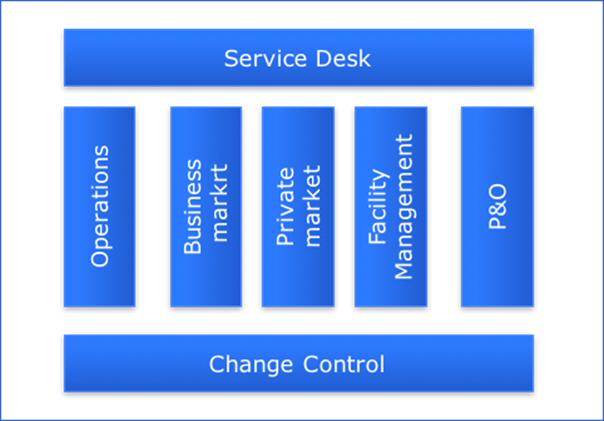
A business line pattern is a split of work between DevOps teams, where all applications are divided across the several lines of business. The interaction of the DevOps teams is nil. Therefore, this is a vertical feature splitting.
In this pattern, the service desk is the SPOC between the customer and the service provider. Operations is the team that monitors the provided services. The change control is a control unit to route business feature requests to the various teams and Go-live. However, this change control function is light since the DevOps teams share only a small part of their features.
The business lines are:
- Commercial market targeting businesses
- Private market targeting natural persons
- Facilities company providing services in the field of equipment, parking, restaurant and other services
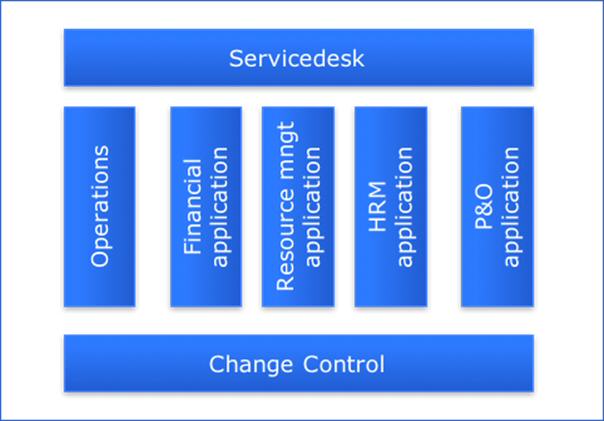
Portfolio pattern
The last commonly used pattern is that of a portfolio orientation. In this organizational form, the teams are clustered to applications that are closely linked by their function. Also this pattern is based on the vertical split of features.
The generic DevOps teams (Service desk), Operations and Change control) als the same as in the business line pattern. Examples of application clusters are financial applications, resource management applications, human resource applications and Personnel & Organization (P&O) applications.
Information value chain pattern
An information value chain pattern is intended to offer a customer information service that provides the information by a number of collaborating teams. This means that for one new report designed by the DevOps reporting team, at least one and up to five DevOps teams will be involved. Therefore, this is a horizontal feature splitting (see article feature splitting).
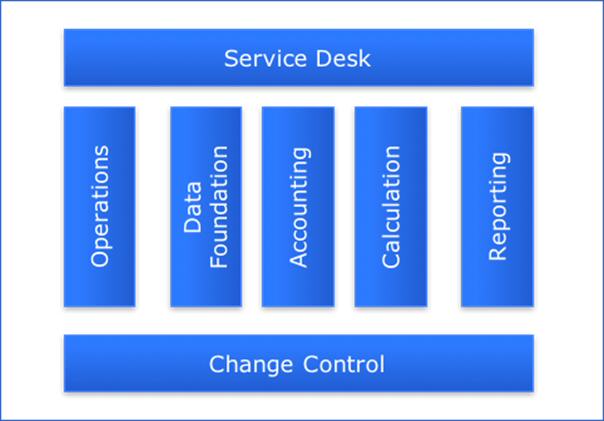
In this pattern, the service desk is the SPOC between the customer and the service provider. Operations is the team that monitors the information services. Data foundation is the team that collects the information files. Accounting is the team that take care of the processing of the information files and performs quality checks. Calculations is the team that performs the calculations required for the reporting. Reporting is the team that supplies the calculated data to the customer in the form of data marts, reporting templates and ad hoc reports. The change control is a control unit to route business feature requests to the various teams and Go-live.
The reason to choose for this pattern is a situation in which the knowledge en know how to build one report is too broad. One could change this pattern and build the DevOps teams on groups of reports. However, in that case one DevOps team must be able to perform the tasks of data collection, data accounting, data calculation and data reporting. Also the consequence could be that these teams do influence each other while working on the same application and information objects.
FAQ
| # | Subject | Question | Answer |
| 1 | Choices | Are there any more patterns? | There will certainly be more patterns. As soon as they are identified, they can be added to this article. |
| 2 | Delay | Does an external change control slow down the DevOps team? | Yes indeed. Wherever possible, the control must be brought back to what is strictly necessary. |
Discuss with us about this article on LinkedIn.
More information
Related Books:
DevOps Best Practices, ISBN: 9789492618078
Agile Service Management with Scrum, ISBN: 9789071501807
Related training sessions:
- DevOps Foundation
- DevOps in practice
- DevOps Master
- Masterclass DevOps Operations
- Masterclass DevOps Application Development
- Masterclass DevOps Architecture
Related Article:


Mogelijk is dit een vertaling van Google Translate en kan fouten bevatten. Klik hier om mee te helpen met het verbeteren van vertalingen.
Laatste artikelen
- De IT-offerte: Waar moet je op letten bij Software en SaaS?
- De ICT-checklist voor het moderne kantoorgebouw
- De paradox van Cloud FinOps Governance: kostenbeheersing in de cloud
- De mens als AI agent: van meester naar slaaf
- Exploratief testen: Agile softwaretesting zonder testscripts
- DRY Principe: Fundament voor Schone Code en Onderhoudbare IT
- Citizen Developer Governance: Veilige Low-Code/No-Code voor medewerkers en compliance
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): Noodstroomvoorziening voor IT-Infrastructuur
- De Cloud Security Baseline: 10 kritieke auditpunten voor AWS, Azure en GCP
- Model Drift: de onvermijdelijke veroudering van AI-modellen
